
On June 9, 2025, the Royal Malaysian Customs Department (RMCD) issued a “Sales Tax Rate Change Transition Guide” (PANDUAN PERALIHAN PERUBAHAN KADAR CUKAI JUALAN), which will come into effect on July 1, 2025. This guide aims to provide a clear understanding of the sales tax treatment during the transition period for the new sales tax rates.
Key Changes and Implementation
The Minister of Finance proposed a revision of sales tax rates for non-essential goods during the 2025 Budget presentation on October 18, 2024. Consequently, some previously exempt goods will become taxable, and existing taxable goods will see their rates amended as stipulated in the Sales Tax (Tax Rate) Order 2025. Generally, the sales tax rate for most taxable goods will be 10%, with exceptions for goods specified at 5% or a specific rate in the Sales Tax (Tax Rate) Order 2025.
Taxation on Manufactured and Imported Goods
Sales tax will be imposed on taxable goods manufactured in Malaysia by registered manufacturers when sold, used, or disposed of, or when imported into Malaysia by any person.
For manufactured goods, the new sales tax rate applies to finished taxable goods when the sales invoice is issued or when the goods are used or disposed of other than by sale, on or after the effective date of the rate change. For imported goods, the new sales tax rate will be applied when the goods are released from Customs control on or after the effective date of the new rate, or according to procedures under the Customs Act 1967.
Generally, the sales tax rate for taxable goods is set at ten percent (10%), except for specific goods listed in the Sales Tax (Tax Rate) Order 2025, which are taxed at 5% or a specific rate.
Sales Tax Rate Transition on Manufactured Goods Likely Scenarios
Here are examples illustrating the taxation on manufactured and imported goods during the transition period:
Situation 1 (Invoice Issued Before New Rate)
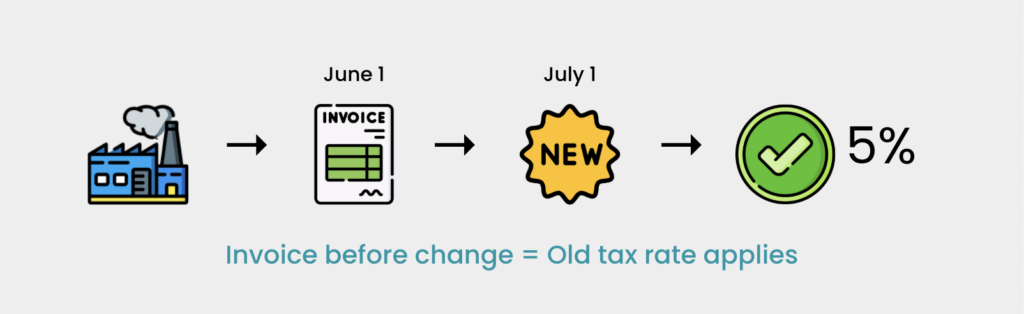
- Registered manufacturer ABC produces goods taxed at 5%. An invoice is issued on June 1, 2025. On July 1, 2025, the tax rate for these goods changes to 10%. The sales tax remains at 5% because the invoice was issued before the effective date of the new sales tax rate.
Situation 2 (Invoice Issued After New Rate)
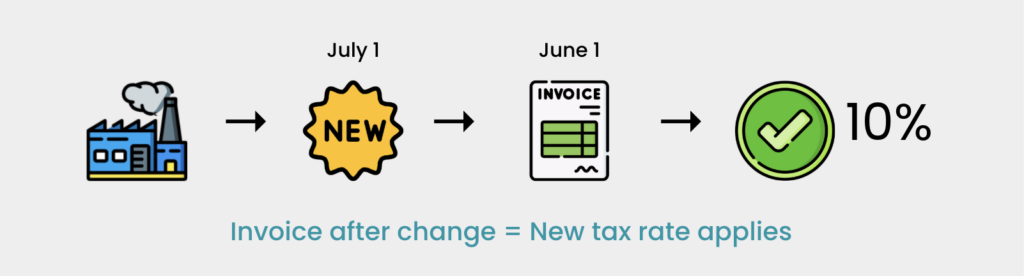
- Registered manufacturer DEF produces goods taxed at 5%. On July 1, 2025, the tax rate for these goods changes to 10%. Manufacturer DEF issues an invoice for the sale of these goods on August 1, 2025. Sales tax at 10% must be imposed because the invoice was issued after the effective date of the new sales tax rate.
Situation 3 (Invoice Issued On New Rate Effective Date)
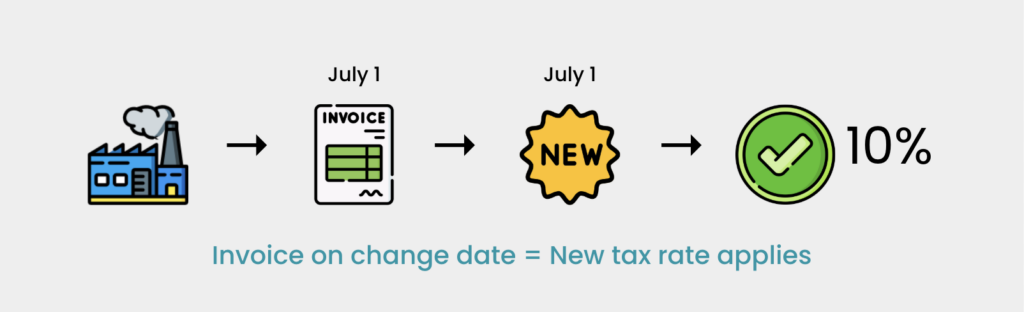
- Registered manufacturer GIH produces goods taxed at 5%. On July 1, 2025, the tax rate for these goods changes to 10%. Manufacturer GIH issues an invoice for the sale of these goods on July 1, 2025. Sales tax at 10% must be imposed because the invoice was issued on the effective date of the new sales tax rate.
Situation 4 (Exempt Goods Becoming Taxable, Company Not Registered)
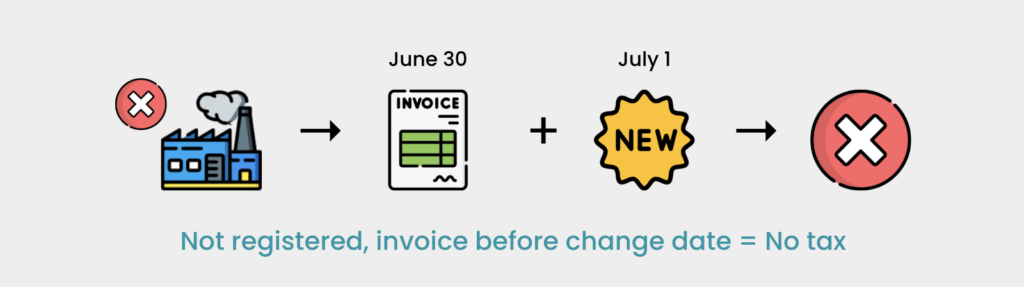
- Company JKL manufactures goods exempt from sales tax and issues an invoice on June 30, 2025. On July 1, 2025, these goods become subject to a new sales tax rate of 5%. The sale is not subject to the new sales tax rate because the invoice was issued before the effective date. Company JKL can only impose the new sales tax rate if it registers as a registered manufacturer on or after the new rate’s effective date.
Situation 5 (Exempt Goods Becoming Taxable, Company Not Registered at Sale Time)
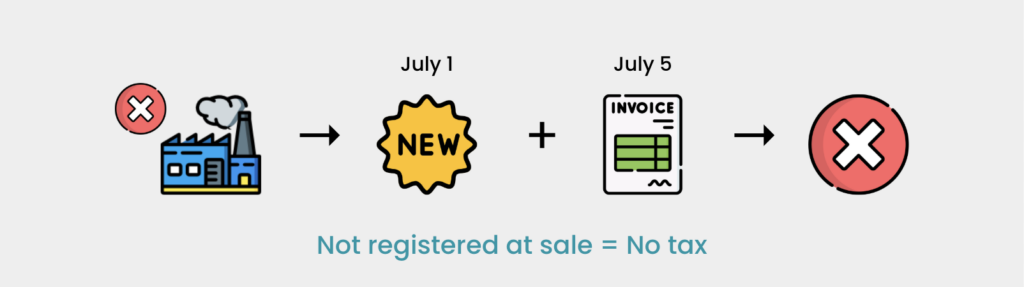
- Company SYH manufactures goods exempt from sales tax and issues an invoice on July 5, 2025. On July 1, 2025, these goods become subject to a new sales tax rate of 5%. Even though the goods are subject to the new rate from July 1, 2025, the company cannot impose the new sales tax rate because it is not a registered manufacturer in accordance with Section 8 of ACJ 2018.
Situation 6 (Registered Manufacturer with Previously Exempt Goods Now Taxable)
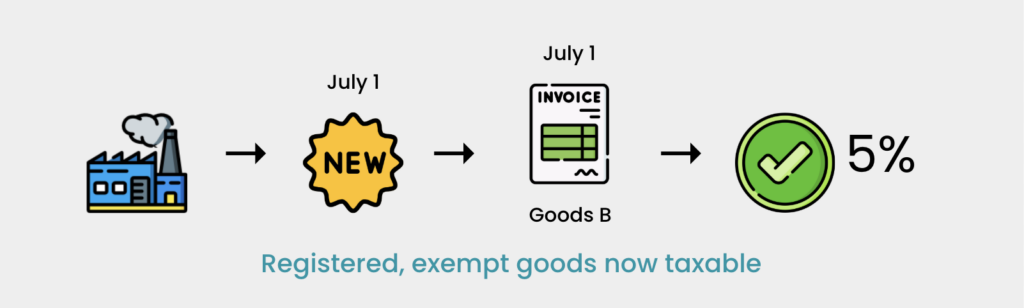
- Company KLM is a registered manufacturer producing two types of finished goods: taxable goods A (10%) and exempt goods B. From July 1, 2025, finished goods B become subject to a new sales tax rate of 5%. Sales invoices issued on or after July 1, 2025, for finished goods B must include the new sales tax because the company is an existing registered manufacturer.
| Situation | Invoice Date | Effective Tax Change Date | Company Type | Old Rate | New Rate | Tax Applied | Reason |
| Invoice issued before new rate | 1 Jun 2025 | 1 Jul 2025 | Registered manufacturer | 5% | 10% | 5% | Invoice issued before new rate took effect. |
| Invoice issued after new rate | 1 Aug 2025 | 1 Jul 2025 | Registered manufacturer | 5% | 10% | 10% | Invoice issued after new rate took effect. |
| Invoice issued on new rate date | 1 Jul 2025 | 1 Jul 2025 | Registered manufacturer | 5% | 10% | 10% | Invoice issued on the effective date of new rate. |
| Exempt goods → taxable, co. not registered | 30 Jun 2025 | 1 Jul 2025 | Not registered manufacturer | Exempt | 5% | 0% | Invoice issued before new rate; company not registered. |
| Exempt goods → taxable, co. not registered at sale time | 5 Jul 2025 | 1 Jul 2025 | Not registered manufacturer | Exempt | 5% | 0% | Goods taxable from 1 Jul, but company not registered (Sec. 8 ACJ 2018). |
| Exempt goods → taxable, co. already registered | On/after 1 Jul 2025 | 1 Jul 2025 | Registered manufacturer | Goods A: 10%, Goods B: Exempt → 5% | 5% (Goods B) | 5% for Goods B | As a registered manufacturer, must impose new tax on invoices from 1 Jul. |
Sales Tax Rate Transition on Imported Goods Likely Scenarios:
Scenario (Imported Goods After New Rate Effective Date)
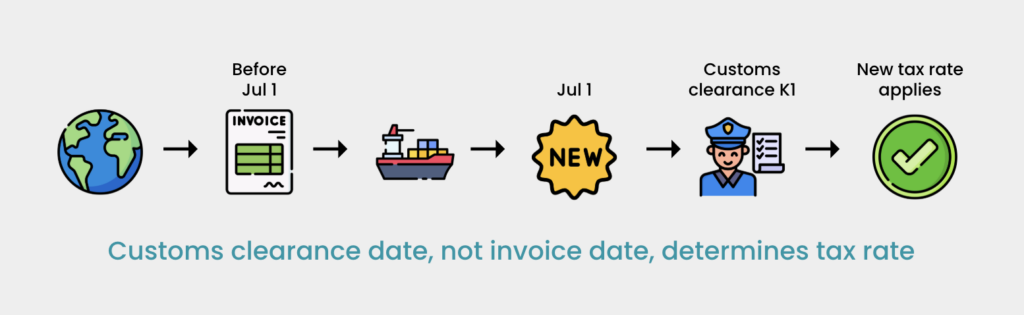
- You purchase goods from overseas, and the invoice was issued before the new sales tax rate’s effective date (July 1, 2025). However, the goods will only be imported after July 1, 2025. The imported goods are subject to the new sales tax rate when they are released from Customs control by the authorized Customs officer. Imports into Malaysia must be declared using Customs Form No.1 (K1), and sales tax for taxable goods is paid using this form.
| Scenario | Invoice Date | New Rate Effective Date | Import/Customs Clearance Date | Tax Applied | Reason |
| Imported goods after new rate | Before 1 Jul 2025 | 1 Jul 2025 | After 1 Jul 2025 | New Rate | Sales tax is imposed when goods are released from Customs, regardless of invoice date. |
Exemptions from Sales Tax Rate Changes
The guide outlines several scenarios regarding the application of the new sales tax rates:
- If an invoice is issued before July 1, 2025, the old sales tax rate applies, even if the goods’ tax rate changes on July 1, 2025.
- If an invoice for taxable goods is issued on or after July 1, 2025, the new sales tax rate will apply.
- For goods that were previously exempt and become taxable on July 1, 2025, sales made by a company that is not a registered manufacturer before or on that date will not be subject to the new sales tax rate.
- However, if a company is already a registered manufacturer and manufactures goods that become taxable on July 1, 2025, sales invoices issued on or after this date for those goods will be subject to the new tax rate.
Taxation on Disposal or Own Use of Manufactured Goods
Sales tax is levied on all taxable goods manufactured by a registered manufacturer, including those disposed of or used for their own purposes. If the disposal or own use occurs on or after the effective date of the new sales tax order, the new rate will apply, regardless of when the disposal or own use was recorded in the company’s accounts.
The application of sales tax for disposal or own use is determined by the effective date of the new sales tax order. If the disposal or own use of such goods occurs on or after the commencement of the order’s enforcement, sales tax will be imposed at the rate stipulated in the Sales Tax (Tax Rate) Order 2025. This applies even if the disposal or own use was recorded in the company’s accounts before the effective date of the order.
Sales Tax Rate Transition on Disposal / Own Use Manufactured Goods Likely Scenarios
Here are examples to illustrate the sales tax treatment for disposal or own use:
Situation 7 (Disposal/Own Use After New Rate Effective Date)
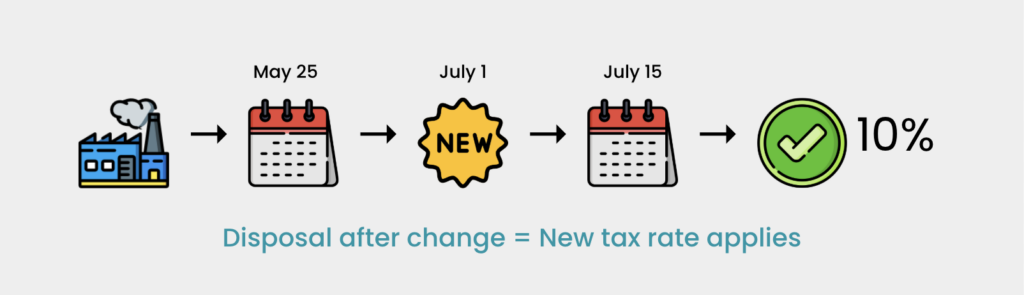
- Registered manufacturer LPV produces goods taxed at 5%. They recorded the disposal or own use of these goods on May 25, 2025. On July 1, 2025, the tax rate for these goods changes to 10%. The actual disposal or own use of the goods occurs on July 15, 2025. In this case, the disposal or own use of the goods is subject to the 10% tax rate because it took place after the effective date of the new order.
Situation 8 (Exempt Goods Becoming Taxable, Disposal/Own Use After Registration and New Rate)
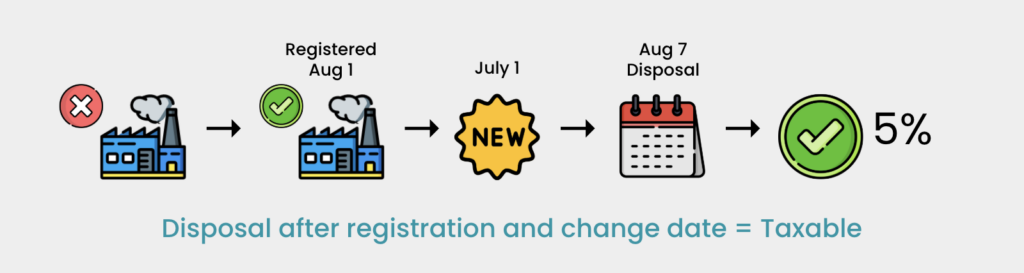
- Manufacturer GBR produces goods that were exempt from sales tax. On July 1, 2025, these goods become taxable at 5%. Manufacturer GBR applies for registration and becomes a registered manufacturer, effective August 1, 2025. They had recorded the disposal or own use of these goods on May 28, 2025, but the actual disposal takes place on August 7, 2025. The disposal or own use of these goods is subject to the 5% tax rate because the disposal or own use occurred after the effective date of the new order and after GBR became a registered manufacturer.
Situation 9 (Exempt Goods Becoming Taxable, Disposal/Own Use After Recording and New Rate, After Registration)
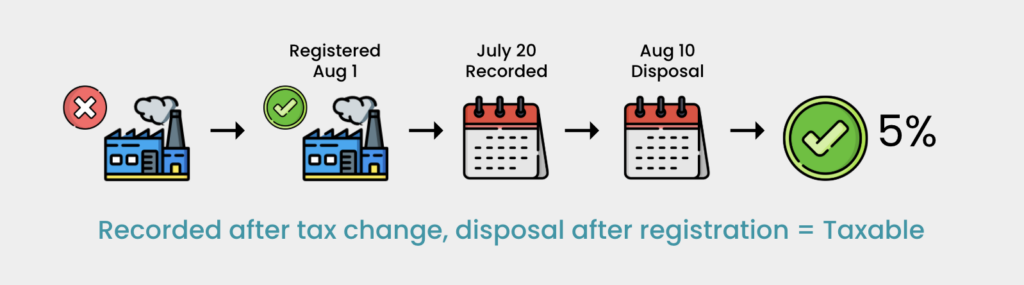
- Manufacturer LHG produces goods that were exempt from sales tax. On July 1, 2025, these goods become taxable at 5%. The disposal or own use of the manufactured goods was recorded on July 20, 2025. Manufacturer LHG applies for and becomes a registered manufacturer, effective August 1, 2025. The disposal or own use of these goods occurs on August 10, 2025. This disposal or own use is subject to the 5% tax rate.
Situation 10 (Exempt Goods Becoming Taxable, Disposal/Own Use Before Registration)
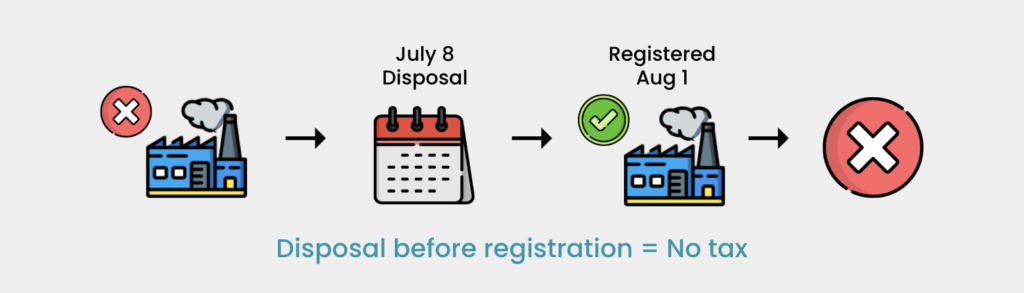
- Manufacturer SJF produces goods that were exempt from sales tax. On July 1, 2025, these goods become taxable at 5%. The disposal or own use of the manufactured goods was recorded on July 20, 2025, and the actual disposal or own use occurred on July 28, 2025. SJF’s registration as a registered manufacturer became effective on August 1, 2025. The disposal or own use of these goods on July 28, 2025, is not subject to the 5% tax because SJF was not yet registered as a manufacturer at the time of disposal or own use.
| Situation | Recorded Date | Effective Tax Change Date | Registration Date | Disposal/Own Use Date | Old Rate | New Rate | Tax Applied | Reason |
| Disposal/own use after new rate effective date | 25 May 2025 | 1 Jul 2025 | Already registered | 15 Jul 2025 | 5% | 10% | 10% | Disposal/own use occurred after the new rate took effect. |
| Exempt → taxable, disposal/own use after registration & new rate | 28 May 2025 | 1 Jul 2025 | 1 Aug 2025 | 7 Aug 2025 | Exempt | 5% | 5% | Disposal/own use occurred after goods became taxable and after company registered. |
| Exempt → taxable, recorded after new rate, disposal after registration | 20 Jul 2025 | 1 Jul 2025 | 1 Aug 2025 | 10 Aug 2025 | Exempt | 5% | 5% | Disposal/own use occurred after both tax change and registration. |
| Exempt → taxable, disposal before registration | 20 Jul 2025 | 1 Jul 2025 | 1 Aug 2025 | 28 Jul 2025 | Exempt | 5% | 0% | Disposal/own use occurred before registration date, so no tax applies. |
Manufacturer Registration Requirements
Any person engaged in manufacturing taxable goods with a total sales value exceeding RM500,000 within a 12-month period is required to register under Section 12 of the Sales Tax Act 2018 (ACJ 2018). Manufacturers whose sales do not meet this threshold may still apply for voluntary registration under Section 14 of the ACJ 2018. The deadline for applying for registration is the last day of the month following the month in which the liability to register arises. Online registration can be done through the MySST portal starting July 1, 2025.
Upon approval, registered manufacturers must impose sales tax on all sales of taxable goods from the effective date stated in the approval letter. They are also required to submit SST-02 statements for each taxable period from the first taxable period indicated in the approval letter.
Certain manufacturing operations are exempt from registration, regardless of the total sales value of taxable goods. These include activities like washing, printing photographs, manufacturing ready-mix concrete, preparing food or beverages by certain service providers, repacking bulk goods into smaller packages, and repairing used goods.
Sales Tax Exemption for Manufacturing Inputs
Under Section 35 of the ACJ 2018, the Minister can exempt certain persons from sales tax as specified in the Sales Tax (Persons Exempted from Payment of Tax) Order 2018 (PCJ(P) 2018). Additionally, the Approved Principal Exporter Scheme under Section 61A(1)(b) of the ACJ 2018 exempts manufacturers from sales tax on raw materials, packaging materials, and components used in manufacturing finished goods that are sales tax-exempt and intended for export or transport to designated areas.
If finished goods that were previously sales tax-exempt become taxable on July 1, 2025, manufacturers who received sales tax exemption on manufacturing inputs for these goods must pay the exempted sales tax on the remaining stock of those inputs. However, this payment is waived if the manufacturer registers and their registration is effective by September 30, 2025. Manufacturers who become registered may then apply for sales tax exemption under Item 1, Schedule C, PCJ(P) 2018 for the purchase or import of raw materials and other manufacturing inputs.
Prepare Your Business for SST 2025 – Free SST Training
If you’re a Malaysian contractor or construction business looking to understand how SST impacts you starting 1 July 2025, learn more: https://www.facebook.com/share/v/16Zc4wTtne/
